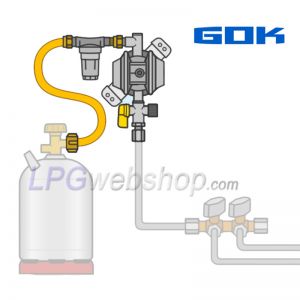
In this article, you will read about pressure regulators for reducing gas pressure from a LPG gas bottle or LPG vapor tank. We explain why this is necessary, what types of pressure regulators exist, and what you need to pay attention to.
The following related tutorials complement this article:
LPG Vapor Tanks for RVs, Caravans, and Food Trucks
LPG Installation in an RV, Caravan, Food Truck, or Motorhome
Assembly Instructions for LPG Cylinder Tanks (Vapor Tanks) in Vehicles
The EN 1949 Standard: The European Standard for Safe LPG Systems in RVs and Caravans
What is an LPG Gas Bottle and what are the different types?
Pressure Regulator, why is it needed?
A pressure regulator is connected (with or without the use of a gas filter and/or high-pressure hose) to the outlet of an LPG vapor tank or gas bottle, with the aim of reducing and regulating the pressure to a stable and low working pressure, in most cases 30 mbar. This pressure reduction is necessary because the pressure coming from the gas tank is many times too high. The pressure in a gas tank varies, depending on temperature, between 1 and 20 bar. This pressure is way too high for the gas appliance(s), such as a stove or heater in your RV. Therefore, it is necessary to reduce the pressure to a constant, safe and low pressure. The current mandatory working pressure for gas systems in RV campers and caravans is 30 mbar. (older LPG systems or in other applications such as food trucks or static caravans sometimes use a working pressure of 50 mbar and sometimes also 39 mbar).
Pressure regulators come in many variations with different connections, output pressures, and different optional accessories.
Pressure regulators can be connected in the following ways:
- Connected directly to the gas bottle (LPG tank). Usually via a female coupling with left-hand thread W21.8 of the type / G.2 / G.4 / G.5 / G.8 / G.12 or (in some countries such as Italy) a female coupling with a slightly smaller left-hand thread, namely W20 of the type G.1). A low-pressure gas hose (EN 16436 Class 2) with a maximum length of 45cm is connected to the outlet of the regulator. This low-pressure gas hose then connects to the fixed rigid gas pipe in the vehicle.
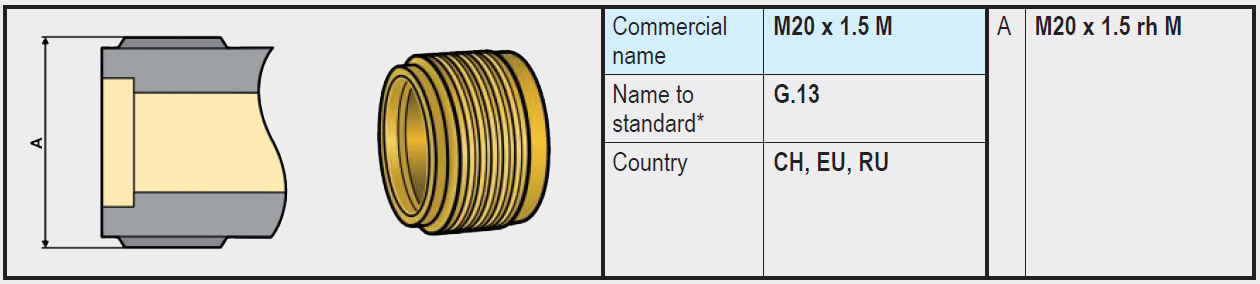
- Remotely connected to the LPG gas bottle valve and mounted on the wall of the gas bottle compartment. The connection between the gas bottle and regulator is made using the previously discussed high-pressure gas hose with a maximum length of 45cm. The inlet of the regulator is usually equipped with a G.13 connection (male M20 thread). The outlet of the regulator is then connected to the fixed rigid gas pipe in the vehicle.
- Like b, but with 2 gas bottles. The inlet of the regulator is equipped with 2 connections (G.13) and a changeover device that ensures the gas bottles are never interconnected and automatically prevents gas from escaping if one of the two gas bottles is not connected.
- Remotely connected to the LPG gas bottle valve (or 2 gas bottles) and mounted on the wall of a sliding tray in the gas bottle compartment, on which the gas bottle(s) and fixed pipe are also mounted. (Gas bottle(s), high-pressure gas hoses, regulator, and partly fixed gas pipe are all mounted together on this sliding tray.) The connection between the gas bottle(s) and regulator is made using the previously discussed high-pressure gas hose with a maximum length of 45cm. The inlet of the regulator is usually equipped with a G.13 connection(s) (male M20 thread). The outlet of the regulator is then connected to the fixed rigid gas pipe on the sliding tray. To connect the gas pipe on the sliding tray to the rest of the fixed gas pipe in the vehicle, a low-pressure gas hose (EN 16436 Class 2 or Class 3) with a maximum length of 75cm is used. In the case of 2 gas bottle connections on the regulator, a changeover device as mentioned earlier must be used.
- As in a, connected directly to the gas bottle (LPG tank). However, with the gas bottle on a sliding tray in the gas bottle compartment. A low-pressure gas hose (EN 16436 Class 2 or class 3) with a maximum length of 75cm is connected to the outlet of the regulator. This low-pressure gas hose then connects to the fixed rigid gas pipe in the vehicle.
Main safety requirements regarding pressure regulators and installation:
- The pressure regulator must comply with the EN 16129 standard.
- The working pressure of a gas system for recreational and domestic use in an RV or caravan must be non-adjustable and 30 mbar.
- The flow capacity of a gas system for recreational and domestic use in an RV or caravan must never exceed 1.5kg/h. For this reason, use a pressure regulator with a maximum flow capacity of 1.5kg/h.
- In the case of using a gas bottle in a gas bottle compartment, the pressure regulator must be used in this compartment.
- The regulator must be equipped with a test connection on the outlet for performing a mandatory leak test of the LPG system downstream of the regulator.
- Where the regulator is not mounted on the LPG gas bottle valve, it must be mounted on the wall of the gas bottle compartment or on the sliding tray.
- In the case of using an LPG tank, the pressure regulator must be fixed directly to the extraction valve.
- Where the regulator is installed on the outside of the vehicle without a housing (e.g., mounted directly on the outlet of an LPG tank in an underfloor mounting situation), the overpressure valve (and optionally the test connection) must be protected against dirt and water.
- If the LPG heating system or another gas appliance is intended to be used while driving the vehicle, it must be prevented that gas (LPG) can escape uncontrolled due to a break in the gas system caused by an accident (see UNECE R122 annex 8). In this case, use a pressure regulator with a crash sensor (and use, in case it is not mounted directly on the LPG gas bottle valve or tank extraction valve, a high-pressure gas hose with a hose rupture valve).
Types of pressure regulators.
We distinguish four main types of pressure regulators below, each with specific characteristics and applications.
Examples of pressure regulators
1. Pressure regulators with direct connection to the outlet of the LPG gas bottle or LPG vapor tank
This is the simplest and most common type. You connect this regulator directly to the outlet of a LPG gas bottle or LPG vapor tank. (with or without the use of a high-pressure gas filter). There are different types of connections on the inlet of this type of regulator. Later in this article, we mention the most common couplings in the EU and in our webshop. (G.1 G.2 G.4 G.5 G.8 G.12)
The outlet of this type of regulator can be:
- A hose barb for an Ø8mm low-pressure gas hose (ideal for one appliance).
- A 1/4" left-hand external thread for a low-pressure gas hose that connects to the low pressure line.
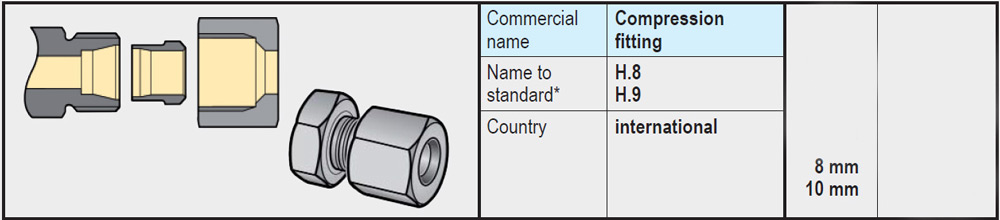
- An 8mm or 10m compression fitting to connect an 8mm or 10mm pipe.
Today, there are also regulators of this type equipped with a crash sensor, as we mention in type 4, making them suitable for use with an LPG tank in or under an RV.
2. Pressure regulators with 8mm compression fitting on the inlet
These regulators are connected via an 8mm pipe to the gas bottle or vapor tank. This type of regulator is generally NOT used in RV campers or caravans, but in food trucks and static caravans.
3. Pressure regulators with M20 connection (G.13) on the inlet (Connection via a high-pressure gas hose)
These regulators are connected to the gas bottle via a high-pressure gas hose or pipe with an M20 connection on the regulator side. Optionally, this type of high-pressure gas hose is also available equipped with a hose rupture valve which ensures that if the hose were to tear (for example during a collision), this rupture valve closes and blocks the gas flow.
However, this type of regulator in combination with a high-pressure gas hose is only suitable for connecting to a gas bottle. According to regulations, a high-pressure gas hose must not be used on an LPG vapor tank. This means that a regulator is connected directly to the outlet (extraction valve) of an LPG vapor tank, without the use of a high-pressure gas hose. That requires a regulator with a different type of connection that fits well with the outlet of the gas tank.
High-pressure gas hoses are available with different types of connections on the inlet (gas bottle side). Later in this article we mention the most common couplings in the EU and in our webshop. (G.1 G.2 G.4 G.5 G.8 G.12)
Optionally (recommended), a high-pressure gas filter is placed between the high-pressure gas hose and the inlet of the regulator (equipped with M20 connections).
4. Pressure regulators with crash sensor
This type is equipped with an additional safety feature: a crash sensor. This is a type of valve on the outlet of the regulator that closes upon impact (for example from a collision) and blocks the gas flow. This makes it safe to use gas while driving, for example for the refrigerator or heater in your RV.
These regulators are often equipped with an M20 connection on the inlet and require the use of a high-pressure gas hose with a hose rupture valve. (as explained later). But nowadays, there are also pressure regulators with crash sensors equipped with a G.2 / G.8 or G.12 connection, allowing them to be connected directly to the outlet of a gas bottle or LPG tank.
Available configurations:
- Horizontal or vertical mounting.
- With 1 or 2 inlets (for 1 or 2 gas bottles).
- With an outlet pressure of 30 or 50 mbar.
Examples:
- GOK Caramatic DriveONE system with crash sensor.
- GOK Caramatic DriveTWO system with crash sensor. This version with two connections has a switch to change between gas bottles, or does so automatically based on available gas pressure.
- GOK Caramatic SafeDrive
- Truma Monocontrol CS
- Truma Duocontrol CS
High-pressure gas hose
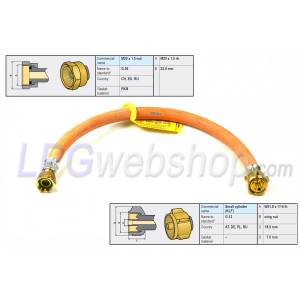
This component makes a connection between the outlet of the gas bottle and the inlet of the pressure regulator. This high-pressure hose is used when the regulator is not connected directly to the outlet of the gas bottle, but is mounted, for example, against the wall or floor of the vehicle. Since this type of gas hose is connected directly to the gas bottle, it must be able to withstand high gas pressure (max 30 bar) and comply with the requirements of EN 16436 Class 3.
A high-pressure gas hose must not be longer than 45 cm, (and according to DVGW G607,) except when the gas bottle(s) are on a sliding tray to be able to pull the gas bottle(s) partly outside the RV to improve the operation of the gas bottle(s) and the regulator is not mounted on this sliding part, but on the fixed part of the vehicle such as the rear wall. In the latter case, the maximum length of the high-pressure gas hose must not exceed 75 cm.
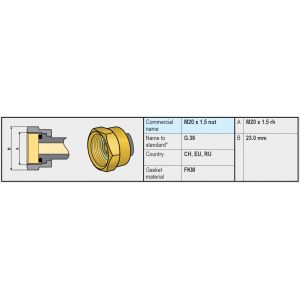
A high-pressure gas hose must be fitted with fixed couplings on both ends. Various types of couplings are possible on the inlet (for example G.1 / G.2 / G.4 / G.8 / G.12) depending on the connection on the gas bottle and the applicable country. And on the other side (outlet side), a high-pressure gas hose is usually equipped with an M20 x 1.5 (G.36) connection, making it suitable for connection to regulators with a (G.13) Male M20 x 1.5 connection on the inlet.
Optionally, a high-pressure gas hose can be equipped with a hose rupture valve, which ensures that the gas supply stops in the event of a rupture.
Most important safety requirements regarding the installation of high-pressure gas hoses:
- A high-pressure gas hose must, by means of proper placement, be protected against mechanical stress, mechanical damage, and overheating.
- A high-pressure gas hose must be well accessible and reachable and must not be placed through or behind walls, above ceilings, or under floors.
- A high-pressure gas hose must continuously rise (run upwards) over its entire length from the connection on the LPG gas bottle to the connection on the pressure regulator. This is to prevent liquid LPG from accidentally entering the regulator.
- A high-pressure gas hose must be designed and mounted in such a way that it cannot accidentally come loose and is under no mechanical stress.
- in the case of gas consumption (heating) while driving, the high-pressure gas hose must be equipped with a hose rupture valve on the inlet side.
High-pressure gas filter
We advise using a gas filter between the gas bottle / vapor tank and the inlet of the pressure regulator. (Do NOT place this downstream of a pressure regulator.) This type of filter is often used in RVs or Caravans to catch paraffin (fats and oils) and any other contamination in liquid form or solid particles (for example sand or iron) and thus prevent them from entering the regulator and the rest of the system. This type of filter is in some cases connected directly to the outlet of a gas tank or gas bottle and is then usually equipped with on one side a female and on the other side a male (G.1 / G.2 / G.4 / G.8 / G.12) connection, so that a regulator with the same connection can be connected directly to it. Or alternatively a high-pressure gas hose. There are also high-pressure gas filters with M20 male and female connections (G.13 and G.36) that are connected directly to the inlet of the regulator. In that case, a high-pressure gas hose is placed between the gas bottle and this high-pressure gas filter.
Examples of high pressure gas hoses and high pressure filters
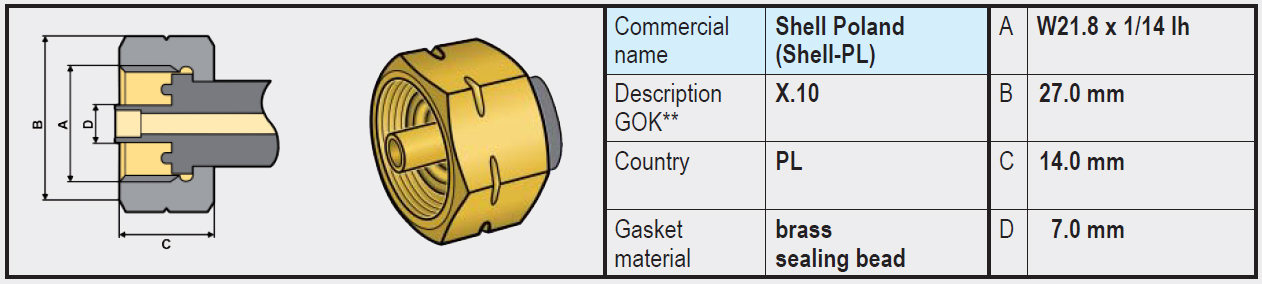
Types of connections on the inlet of regulators (or high-pressure gas hose) (G.1 / G.2 G.4 G.5 G.8 / G.12)
Unfortunately, there are many different types of connections on LPG gas bottles. Depending on the country of application, one type or another is used. Therefore, it is important to know and understand the connection on the gas bottle and gas tank.
In most European countries, a variant of the SHELL connection with W21.8 Left-hand thread is used. The difference usually lies in the type of seal and central fit.
In this section, we cover the most common types of connections such as: G.1 (W20 left-hand thread MALE) and the SHELL connections G.2 G.4 G.5 G.8 and G.12 (W21.8 x 1/14, M22 left-hand thread MALE), the most common connections in Europe.
Within the SHELL connections (W21.8 Left-hand thread), there are different variants, the main differences being in the sealing method (G.2 G.4 G.5 G.8 / G.12).
Difference between G.1 / G.2 G.4 G.5 G.8 / G.12
- Types G.2 / G.4 / G.5 / G.8 (W21.8 x 1/14 left-hand thread): These variants are very similar and on the gas bottle side have no rubber seal and are completely made of brass. The sealing is on the side of the regulator or high-pressure gas hose, often in the form of a rubber or plastic ring.
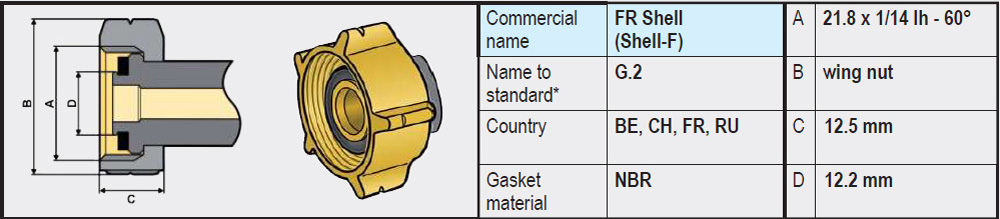
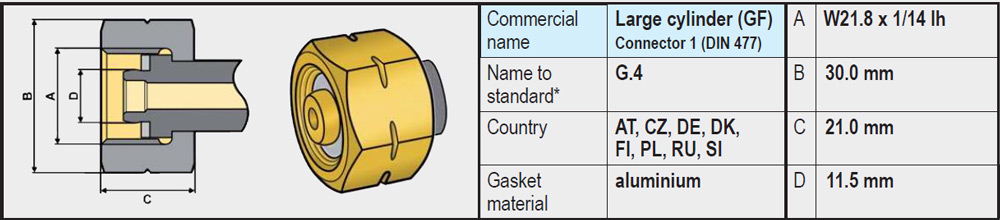
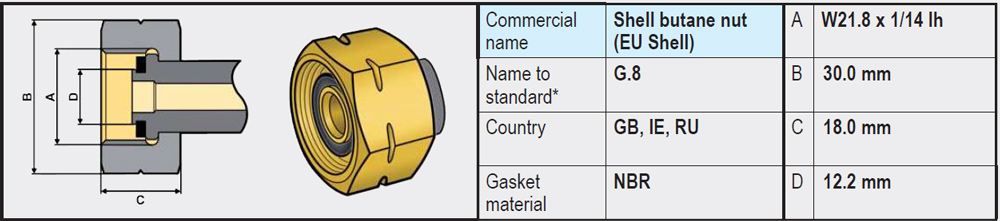
- Type G.12 (W21.8 x 1/14 left-hand thread): Differs slightly from the connections mentioned above and on the gas bottle side does have a recessed rubber sealing ring. The coupling of the regulator has an integrated annular brass rim that is pressed into the rubber ring on the gas bottle side when tightened and provides a seal.
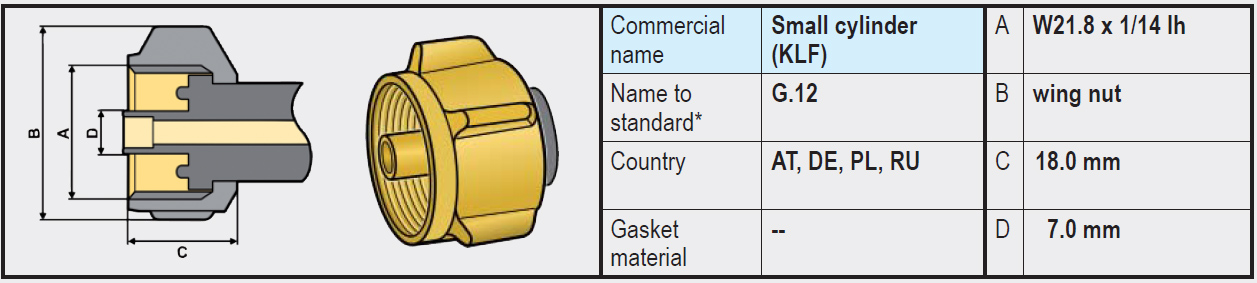
Note: It is not possible to connect a regulator (or high-pressure gas hose) with a G.12 coupling (with integrated annular brass rim) directly to an LPG gas bottle with type G.2 / G.4 /G.5 / G.8 (without rubber); a seal will not be created (brass on brass). In that case, use an adapter (G.5 to G.12) that we offer in our webshop.
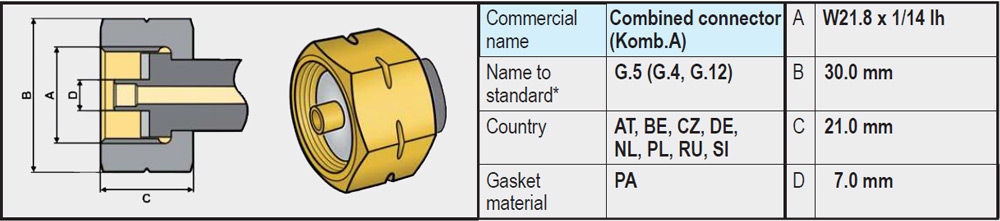
A regulator (or high-pressure gas hose) with a G.5 coupling, on the other hand, will fit on a gas bottle with a G.12 connection. The G.5 connection is therefore also called a Kombi coupling, because it fits both on a G.2, G.4, G.8 and on a G.12.
Exceptions are:
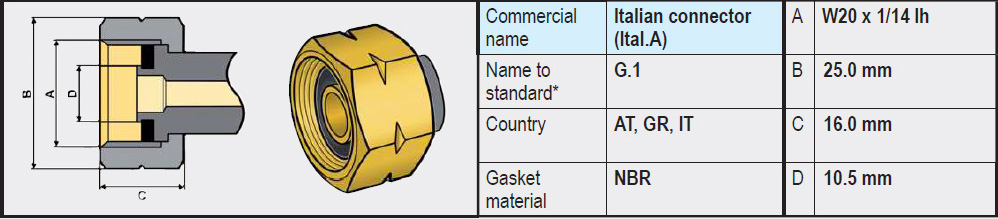
In Italy, Greece, Austria, Slovenia, the G.1 connection is often used, which uses left-hand W20 thread instead of left-hand W21.8 thread. It therefore looks very much like a SHELL connection, but is slightly smaller. In our webshop, we also offer adapters that make it possible to reduce an LPG gas bottle with the slightly larger W21.8 thread to W20, so that it can be used in an Italian RV and connected to a G.1 regulator (or high-pressure gas hose).
- Type G.1 (W20x1/14 Left-Hand Thread) Widely used in the countries (Italy, Greece, Austria, Slovenia). Has no rubber seal on the gas bottle side and is completely made of brass. The sealing is on the side of the regulator or high-pressure gas hose, often in the form of a rubber or plastic ring.
In addition, there are connections of the POL and Clip-on type, but since they are not often used in European countries, we will not consider them further.
Examples of Adapters for Gas Bottles
The low pressure line
After the pressure has been reduced to 30 or 50 mbar, the gas can be distributed and transported to the gas appliances. This part of the installation is called the "low pressure line". Depending on the application, this line can be simple or extensive.
This article is protected by copyright. (Partially) copying this article is prohibited.
Disclaimer
The information in this article is intended solely as an aid and has been compiled to align as well as possible with applicable regulations and guidelines. National regulations may differ or impose additional requirements. Installers and users are themselves responsible for (having) the gas installation checked and complying with applicable local laws and regulations. Always consult a certified professional for this.
Despite the care with which this information has been compiled, there is the possibility of errors and omissions. No rights can be derived from this article. The most recent and local official standards and regulations are always leading.
In addition to this specific disclaimer, our general disclaimer also applies, the link to which can be found in the menu in the footer (page end).